HEALTH/SCIENCE
The Dark Side of Nature: 20 Frightening Parasite Facts
Published
7 months agoon

Shutterstock
Parasites are some of the most fascinating yet terrifying organisms on Earth. They survive by exploiting their hosts, often leading to bizarre and disturbing consequences. From mind-controlling fungi to worms that consume their hosts from within, parasites showcase a wide range of horrifying behaviors. While many people think of parasites as mere nuisances, their complex life cycles and interactions with their hosts are nothing short of extraordinary. Here, we explore 20 of the weirdest and scariest facts about parasites that will make your skin crawl.
Zombie Ants
Shutterstock
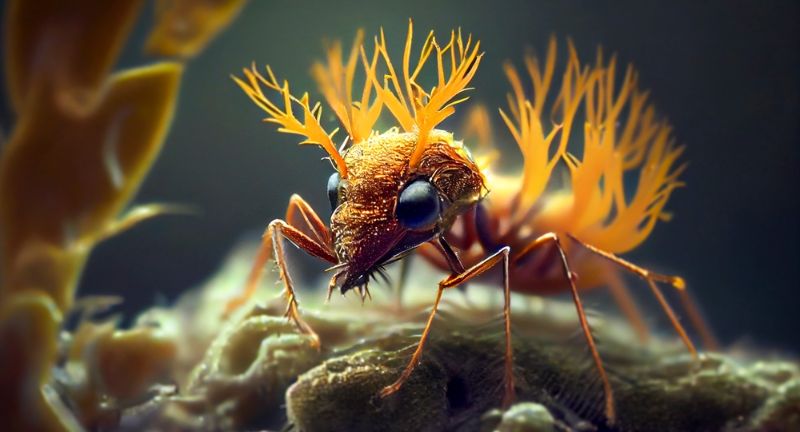
The Ophiocordyceps fungus infects ants, taking over their central nervous system. This fungal invasion forces the ant to climb vegetation and attach itself before eventually dying. The fungus then sprouts from the ant’s body, spreading spores to infect other ants. This bizarre and terrifying manipulation turns the ant into a zombie, entirely controlled by the parasitic fungus.
Brain-Eating Amoeba
Shutterstock
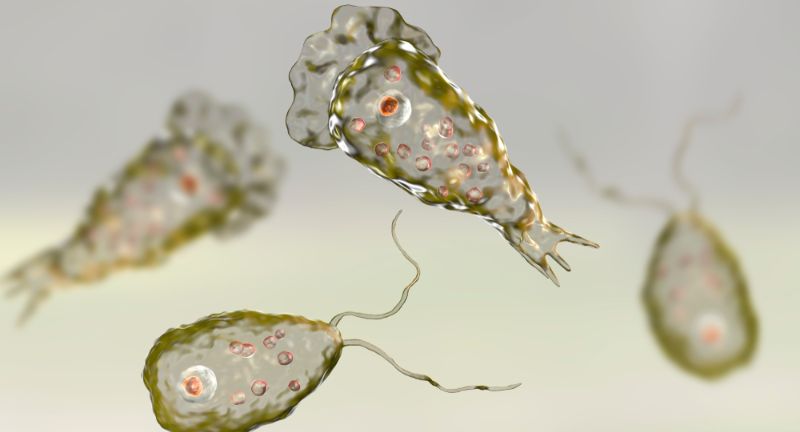
Naegleria fowleri, known as the brain-eating amoeba, is found in warm freshwater environments. It enters the human body through the nose and travels to the brain, causing primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM). This infection leads to severe brain swelling and is almost always fatal. Despite its rarity, the high mortality rate makes it a terrifying parasite.
Mind-Controlled Crickets
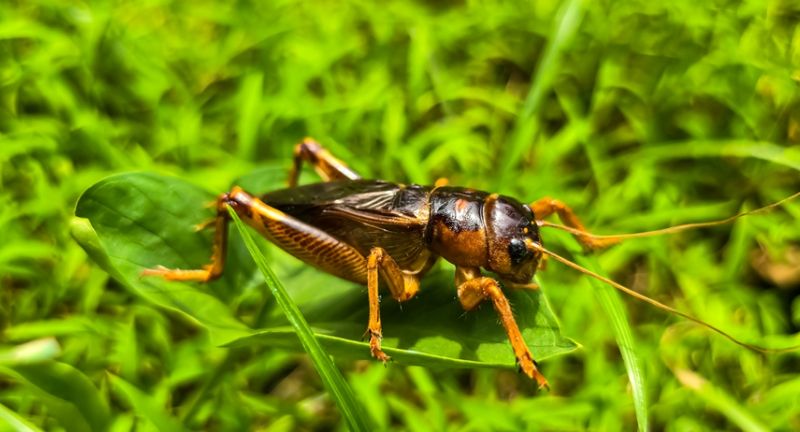

Shutterstock
Parasitic hairworms infect crickets and take over their nervous system, compelling them to seek water. Once near a water source, the cricket jumps in and drowns, allowing the hairworm to emerge and continue its life cycle. This drastic behavioral manipulation is both fascinating and horrifying. The parasite’s control over its host demonstrates the extreme adaptations of parasitic life.
Leucochloridium Paradoxum
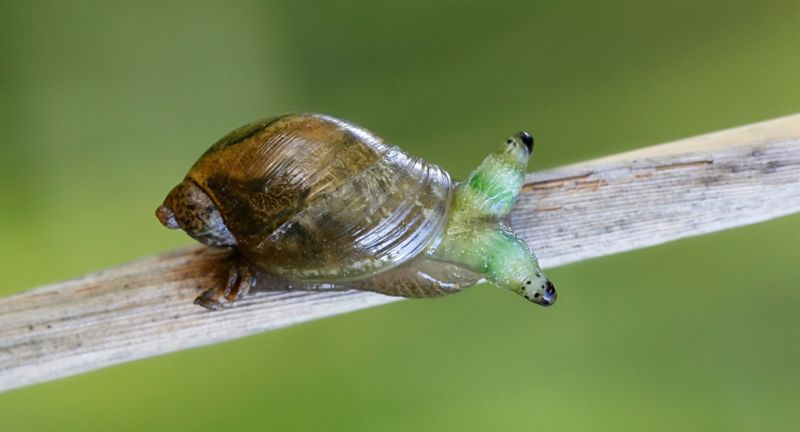

Shutterstock
The flatworm Leucochloridium paradoxum infects snails, causing their tentacles to pulsate and resemble caterpillars. Birds mistake these infected snails for food, eat them, and become the parasite’s next host. The flatworm’s ability to manipulate the appearance and behavior of its host is astounding. This cycle ensures the parasite’s survival and spread through different species.
Tongue-Eating Louse
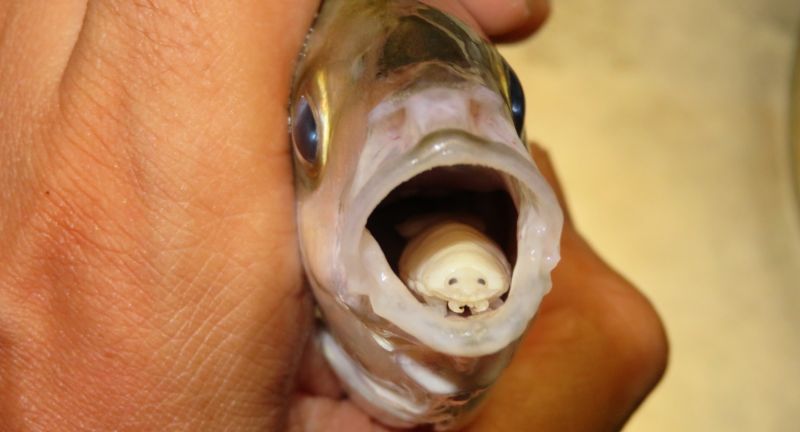

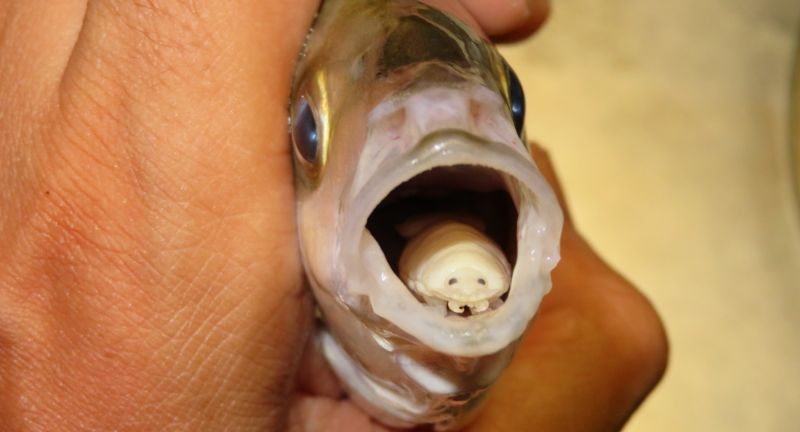
Shutterstock
Cymothoa exigua, the tongue-eating louse, enters fish through their gills and attaches to their tongue. The parasite consumes the fish’s tongue and then physically replaces it. This parasitic relationship is unique and particularly disturbing as the louse continues to function as the fish’s tongue. The fish can still feed, but it now relies on its parasitic invader for a critical function.
Toxoplasma Gondii

Shutterstock
Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite capable of infecting nearly all warm-blooded animals, including humans. It causes infected rodents to lose their fear of cats, making them easy prey and ensuring the parasite’s life cycle continues. This parasite has also been linked to subtle behavioral changes in humans. The potential impact on human mental health adds to its eerie reputation.
Liver Fluke

Shutterstock
Liver flukes infect a variety of mammals, including humans, often causing significant liver damage. They are typically contracted by consuming raw or undercooked fish containing the parasite. Once inside the host, liver flukes can cause severe health issues such as bile duct inflammation and liver cirrhosis. The parasitic infection can be long-term and requires proper treatment to prevent serious complications.
Guinea Worm
Wikipedia
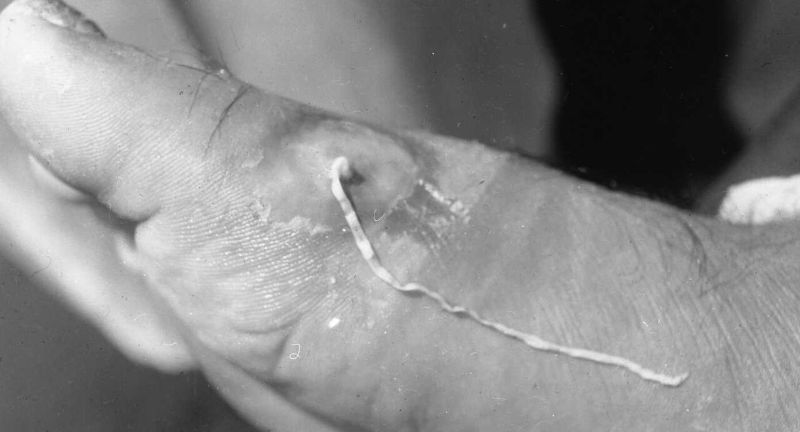
The Guinea worm grows up to three feet long inside its human host. It eventually emerges through painful blisters on the skin, often requiring careful extraction over several weeks to avoid breaking the worm. If the worm breaks, it can cause severe inflammation and secondary infections. This slow, agonizing process makes Guinea worm disease one of the most excruciating parasitic infections.
Elephantiasis
Shutterstock
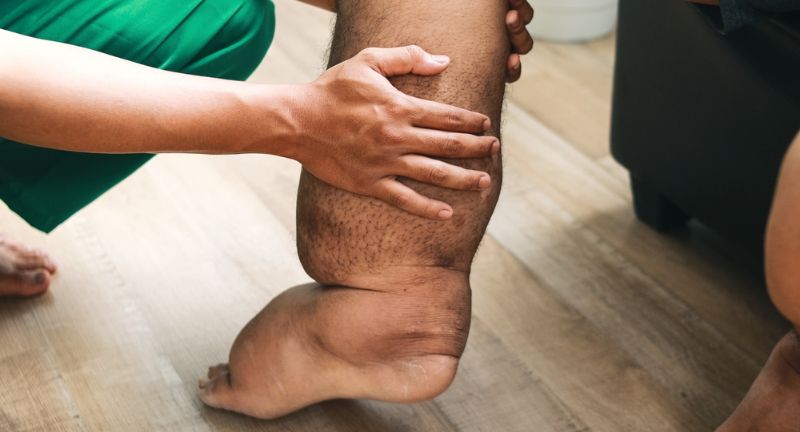
Elephantiasis is caused by filarial worms that block the lymphatic system, leading to extreme swelling of the limbs and genitals. This condition can cause severe physical and emotional distress, making daily activities difficult. The chronic inflammation and tissue swelling can lead to permanent disability. It’s a stark reminder of the devastating impact parasitic infections can have on human life.
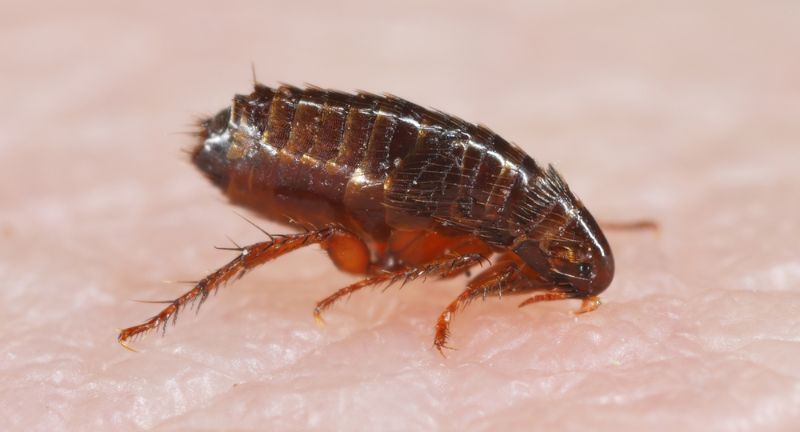
Cat Flea

Shutterstock
Cat fleas are notorious for their ability to transmit tapeworms to pets and humans. They are incredibly resilient and can jump up to 150 times their body length to find a host. Once they latch onto a host, they feed on blood, causing itching and potential allergic reactions. Their persistence and ability to infest homes make them a significant nuisance and health concern.
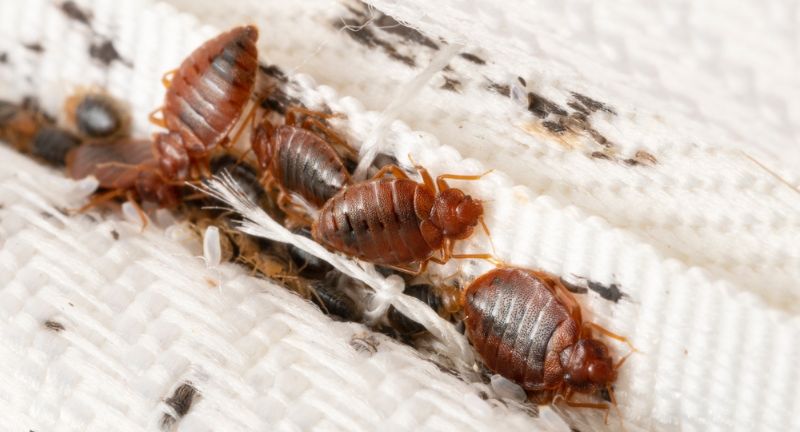
Bedbugs

Shutterstock
Bedbugs are tiny insects that feed on human blood, often during the night. Their bites can cause itchy welts, allergic reactions, and significant psychological distress. Bedbugs are elusive and challenging to eradicate, often hiding in cracks and crevices of beds and furniture. Their ability to rapidly reproduce and spread makes infestations particularly difficult to control.
Dracunculiasis

Shutterstock
Dracunculiasis, also known as Guinea worm disease, is transmitted through drinking water containing infected water fleas. The worm matures inside the host and eventually emerges through painful skin blisters. Extraction of the worm can take weeks, during which severe pain and inflammation occur. This parasitic infection is incredibly debilitating and requires careful prevention and treatment strategies.
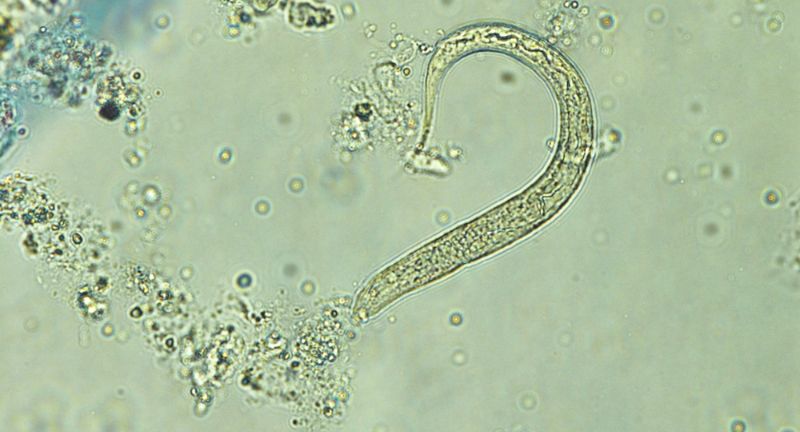
Hookworms
Shutterstock
Hookworms penetrate the skin, usually through bare feet, and travel to the intestines. They attach to the intestinal walls and feed on the host’s blood, leading to severe anemia and malnutrition. Chronic hookworm infection can cause significant health issues, particularly in children, affecting growth and cognitive development. Proper sanitation and footwear can help prevent this parasitic infection.
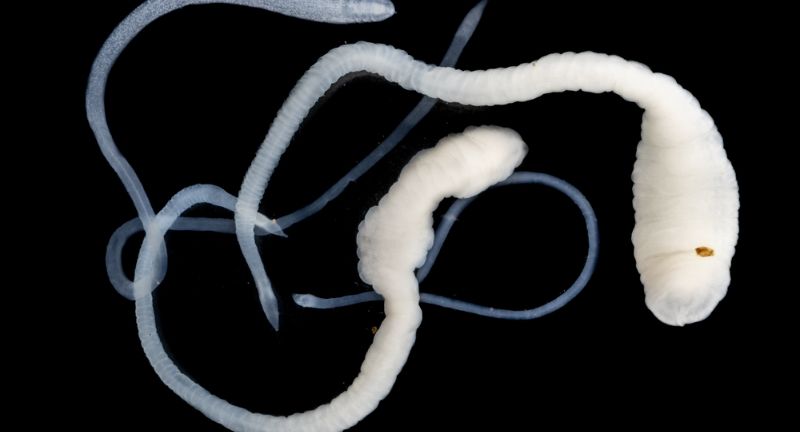
Tapeworms
Shutterstock
Tapeworms can grow up to 30 feet long inside the intestines of their host. They absorb nutrients directly through their skin, often causing malnutrition and digestive issues for the host. Tapeworm infections are typically contracted by consuming undercooked or contaminated food. The sheer size and longevity of these parasites within a host’s body are both fascinating and disturbing.
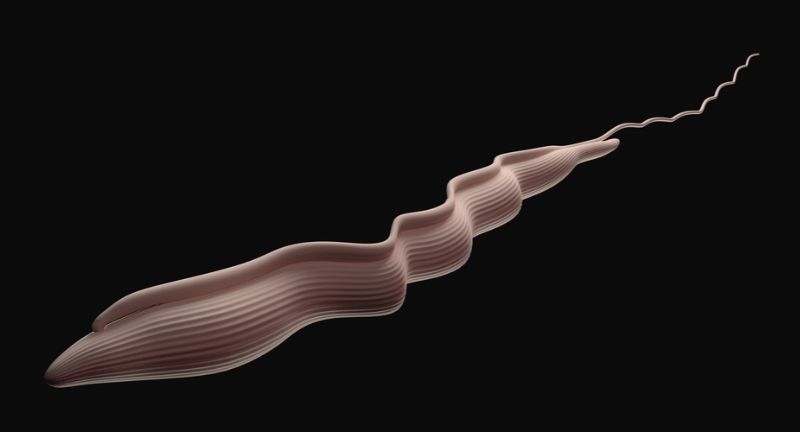
Trypanosoma Brucei
Shutterstock
Trypanosoma brucei is the protozoan parasite responsible for African sleeping sickness. This disease is characterized by severe neurological symptoms, including disruption of the sleep cycle. If left untreated, it often leads to death. The parasite’s ability to evade the immune system and its devastating impact on the host’s brain make it a particularly feared pathogen.
Parasitic Wasps

Shutterstock
Parasitic wasps lay their eggs inside or on the bodies of other insects. The wasp larvae then feed on the host from the inside out, eventually killing it. This gruesome reproductive strategy ensures the survival of the wasp’s offspring. The sight of an insect being consumed from within is both terrifying and a testament to the harsh realities of nature.
Loa Loa

Shutterstock
Loa loa, known as the African eye worm, travels through the subcutaneous tissues of its host. It can often be seen moving across the eyeball, causing significant discomfort and eye damage. Infections are typically contracted through the bites of infected deer flies. The sight of a worm moving across the eye is particularly unsettling for those affected.
Sparganosis

Shutterstock
Sparganosis is caused by consuming infected water or undercooked meat containing Spirometra larvae. The larvae migrate through the body and can sometimes emerge through the skin or eyes. This parasitic infection can cause painful and disfiguring lesions. The unpredictability of where the larvae will travel and emerge makes sparganosis a particularly disturbing parasitic disease.
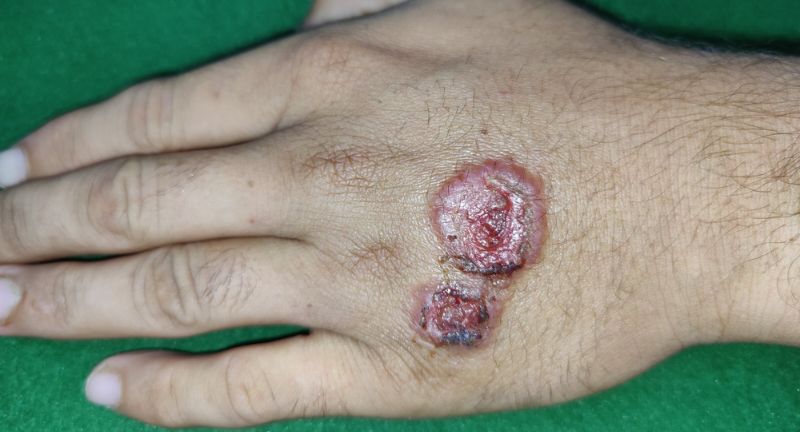
Leishmaniasis
Shutterstock
Leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of infected sandflies. This parasitic disease can cause severe skin ulcers or damage to internal organs, depending on the Leishmania species involved. The disfiguring skin lesions and potential for fatal organ damage make leishmaniasis a significant public health concern. Prevention and treatment are essential to control the spread of this debilitating disease.
Echinococcus
Shutterstock
Echinococcus tapeworms cause hydatid disease, forming cysts in the liver, lungs, or other organs. These cysts can grow large and cause serious health issues if they rupture. Surgical removal is often required to treat the infection and prevent life-threatening complications. The potential for cysts to burst and spread infection throughout the body is particularly alarming.
Conclusion

Shutterstock
Parasites remind us of the often hidden and complex interactions within the natural world. Their ability to manipulate, control, and harm their hosts in such diverse ways is both fascinating and frightening. Understanding these organisms better can help us develop strategies to prevent and treat parasitic infections. While their existence might be unsettling, parasites play a crucial role in ecosystems and biological research. They continue to challenge our understanding of survival and adaptation in the animal kingdom.




