ANIMALS
30 Rarest Animal From Around The World
Published
12 months agoon

Shutterstock
Dive into the fascinating and delicate facets of the animal kingdom with this captivating exploration of thirty critically endangered species, each facing unique challenges to their survival. Travel from the deep sea to dense forests and remote islands, where these animals are crucial components of the complex tapestry of global biodiversity. Their stories go beyond mere tales of endurance; they highlight the profound impact of human activity on the natural world. This journey through the rarest animal species underscores the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect these precious creatures and their habitats, ensuring their well-being for generations to come.
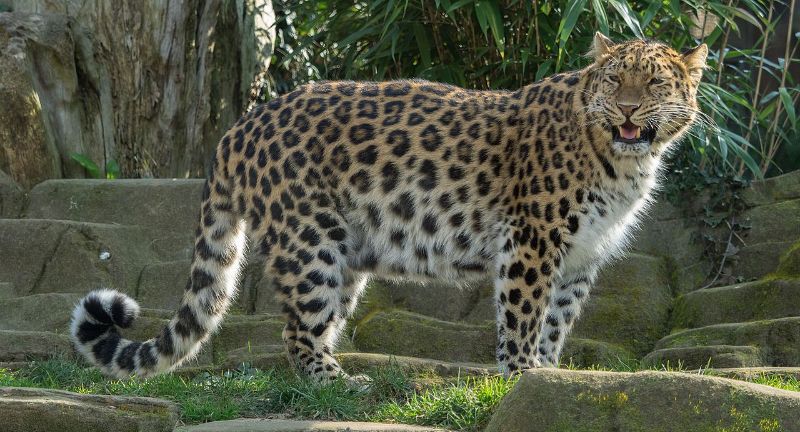
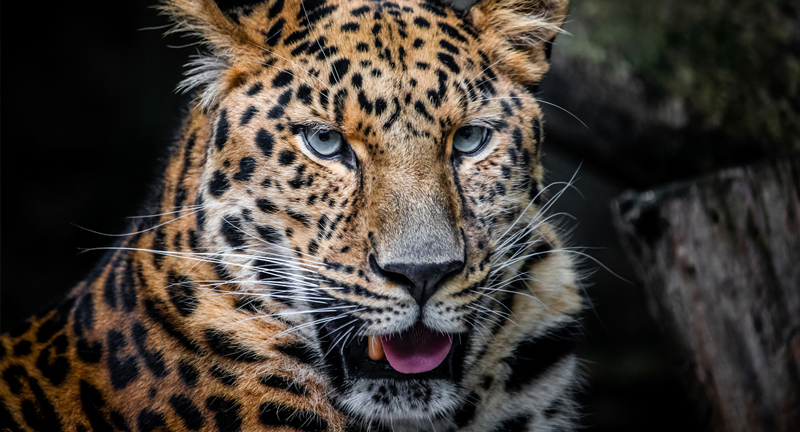
Amur Leopard

Wikipedia
The Amur Leopard, residing in the temperate forests of the Russian Far East and northeastern China, teeters on the edge of extinction, with fewer than 100 individuals believed to be left in the wild. This solitary, nocturnal predator faces threats including habitat loss, poaching for its unique spotted fur, and a decline in prey numbers. Conservation strategies for this species include protecting its habitat, enforcing anti-poaching laws, and breeding programs aimed at increasing their numbers. The survival of the Amur Leopard is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance of its environment.
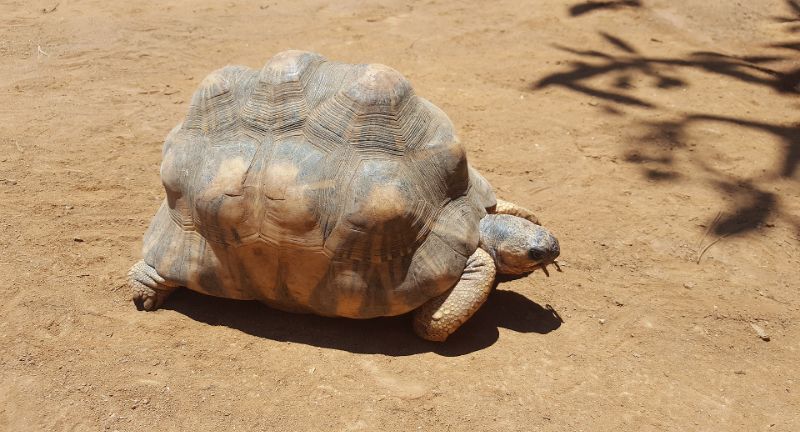
Ploughshare Tortoise

Wikipedia
The Ploughshare Tortoise, also known as the Angonoka Tortoise, found only in Madagascar, is critically endangered. Its unique golden shell has made it highly sought after in the illegal pet trade, significantly contributing to its dwindling population. Conservation efforts are focused on combating poaching, safeguarding its natural habitat, and carrying out breeding programs to increase its numbers in the wild. The fight to save the Ploughshare Tortoise underscores the devastating impact of the global illegal wildlife trade on species survival.
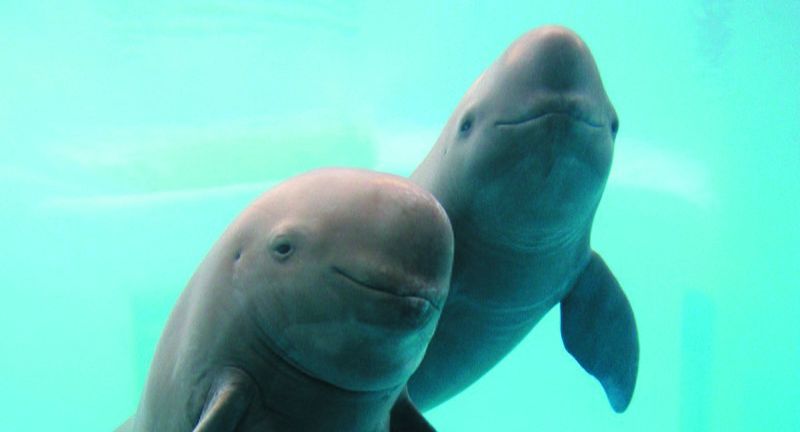
Yangtze Finless Porpoise

Wikipedia
The Yangtze Finless Porpoise, the only freshwater porpoise species, is critically endangered, residing in the Yangtze River in China. Celebrated for its intelligence and playful demeanor, this species is threatened by habitat degradation, pollution, and illegal fishing. Conservation initiatives are directed towards establishing protected areas and researching their behavioral and ecological characteristics to inform protective strategies. The status and health of the Yangtze Finless Porpoise are indicative of the broader ecological health of the Yangtze River ecosystem.
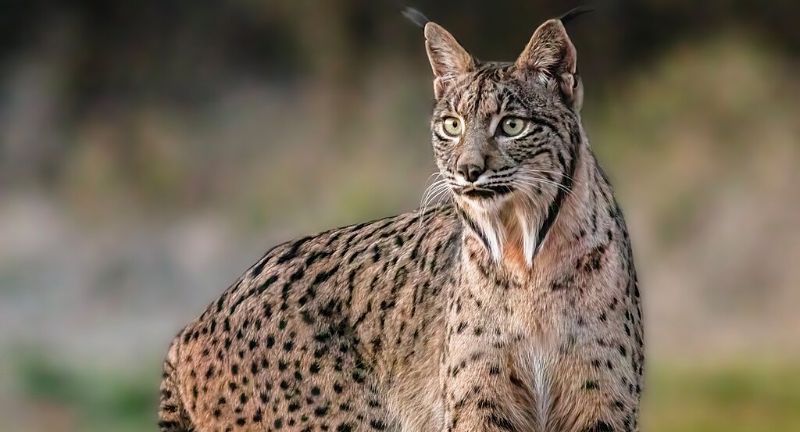
Iberian Lynx

Wikipedia
The Iberian Lynx, once labeled as the most endangered cat species globally, has seen its population numbers increase, thanks to dedicated conservation efforts in Spain and Portugal. Actions like the restoration of their natural habitats, managing the populations of rabbits (their primary food source), and successful breeding programs have been pivotal in their recovery. Nonetheless, issues such as habitat fragmentation and road accidents continue to threaten their existence. The resurgence of the Iberian Lynx serves as a motivational tale for conservationists working to safeguard endangered species.
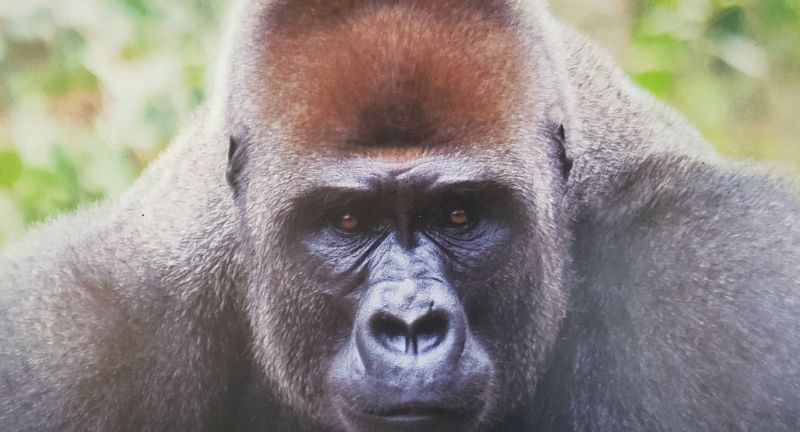
Cross River Gorilla

Wikipedia
The Cross River Gorilla, with an estimated population of just 200 to 300 individuals, is the most endangered among the gorilla subspecies. It inhabits the dense forests and mountainous regions straddling the border between Nigeria and Cameroon. These gorillas are under threat from habitat destruction, poaching, and diseases transmitted by humans. Conservation efforts focus on protecting their habitat, implementing anti-poaching patrols, and promoting sustainable livelihoods for surrounding communities to reduce dependence on the forest. The survival of the Cross River Gorilla is crucial for preserving the biodiversity of the area.
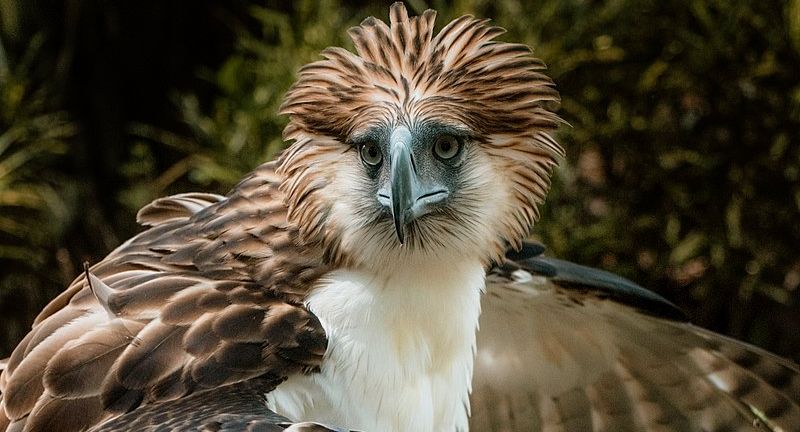
Philippine Eagle

Wikipedia
The Philippine Eagle, renowned as one of the largest and most formidable birds of prey, faces critical endangerment, with deforestation and hunting posing significant threats to its survival in its native Philippines habitat. Celebrated for its majestic presence and impressive strength, this eagle serves as a vital apex predator in the ecosystem. Conservation endeavors entail safeguarding habitats, implementing breeding programs, and raising awareness among communities about the significance of preserving this national emblem. The battle to protect the Philippine Eagle represents a pivotal component of broader conservation initiatives aimed at safeguarding the Philippines’ diverse biodiversity.
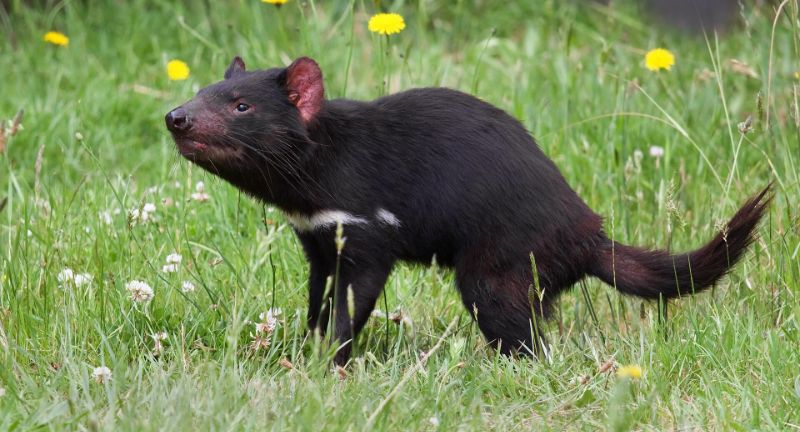
Tasmanian Devil

Wikipedia
The Tasmanian Devil, indigenous to Tasmania, is recognized for its aggressive behavior and distinctive, unsettling vocalizations. This marsupial confronts a formidable threat from a contagious facial tumor disease, resulting in a severe population decline. Conservation initiatives focus on disease control, captive breeding, and reintroduction schemes. Preserving the Tasmanian Devil is paramount for sustaining the ecological equilibrium of Tasmania’s ecosystems.
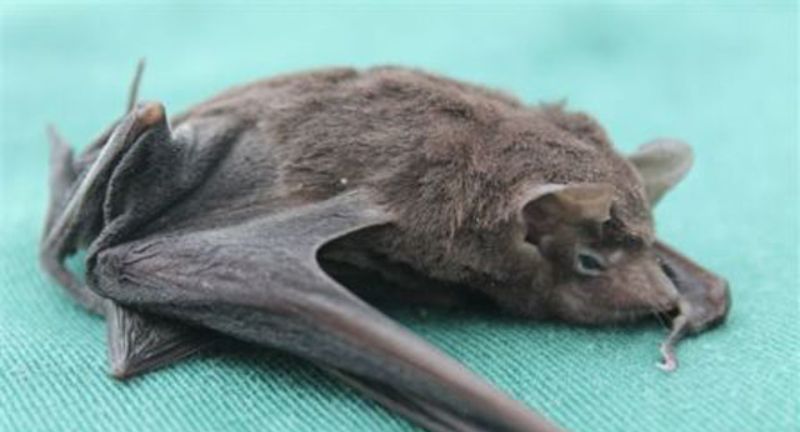
Seychelles Sheath-tailed Bat

Wikipedia
With fewer than 100 individuals remaining, the Seychelles Sheath-tailed Bat is critically endangered, facing threats from habitat loss and predation. This small bat, unique to the Seychelles, highlights the island nation’s rich biodiversity. Conservation efforts are focused on protecting and restoring its natural habitat and conducting research to better understand the species’ needs. The preservation of the Seychelles Sheath-tailed Bat is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance and diverse wildlife of the Seychelles.
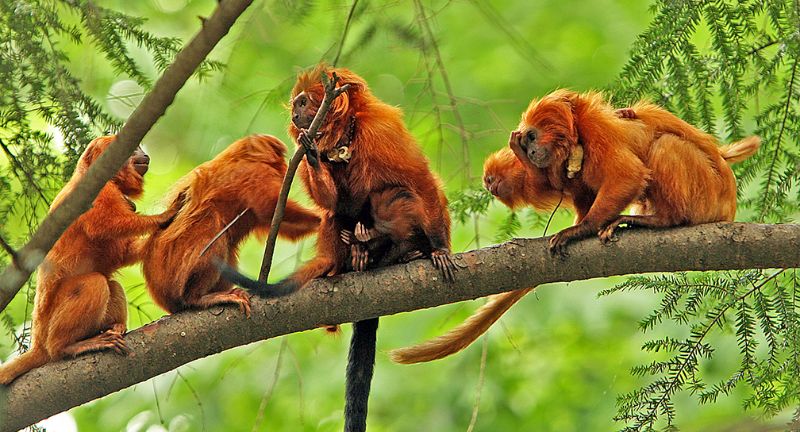
Golden Lion Tamarin

Wikipedia
The Golden Lion Tamarin, notable for its vivid golden-orange fur and expressive facial features, is indigenous to the Atlantic Forest of Brazil. This species has become endangered, with numbers drastically reduced by habitat destruction and the illegal pet trade. Conservation initiatives, including reforestation and the establishment of biological reserves, have contributed to a gradual increase in their population. Serving as a conservation icon for the Atlantic Forest, one of the world’s most endangered ecosystems, the Golden Lion Tamarin is crucial to its preservation efforts.
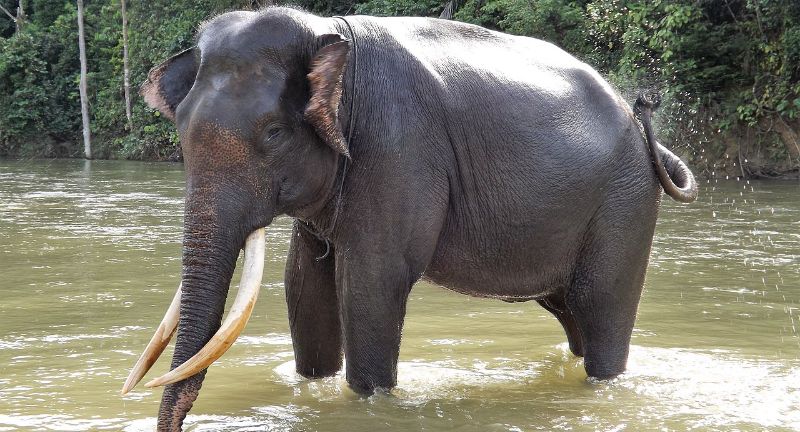
Sumatran Elephant

Wikipedia
The Sumatran Elephant, a unique subspecies of the Asian Elephant, is critically endangered, primarily due to habitat reduction, rampant deforestation, and increasing human conflicts. Found on Indonesia’s island of Sumatra, these elephants play a vital role in maintaining the equilibrium of the forest ecosystem. Protective measures for these elephants include habitat conservation, enforcement of poaching bans, and the creation of strategies to minimize human-elephant conflicts. The survival of the Sumatran Elephant is crucial for preserving the biodiversity of the region.
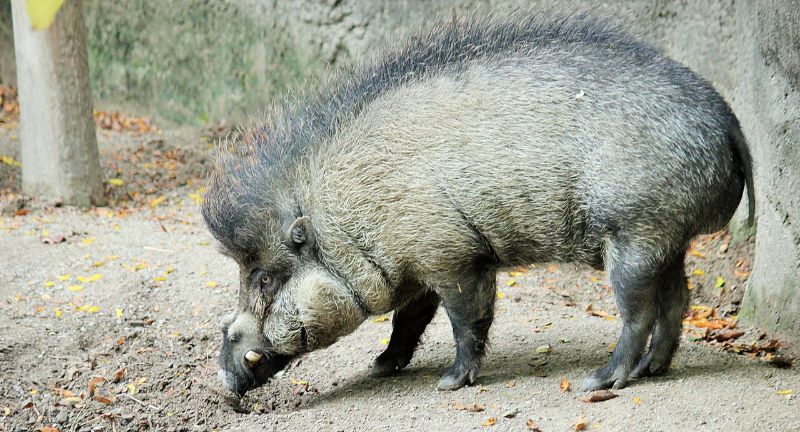
Visayan Warty Pig

Wikipedia
The Visayan Warty Pig, originating from the Visayas islands in the Philippines, is critically endangered due to habitat loss, hunting, and the invasion of non-native species. Distinguished by distinctive facial warts and hair tufts, this pig plays a vital role in its ecosystem. Conservation measures include habitat restoration, captive breeding programs for eventual reintroduction, and engaging local communities in the protection of these animals. Efforts to save the Visayan Warty Pig highlight the importance of maintaining biodiversity in the Philippines.
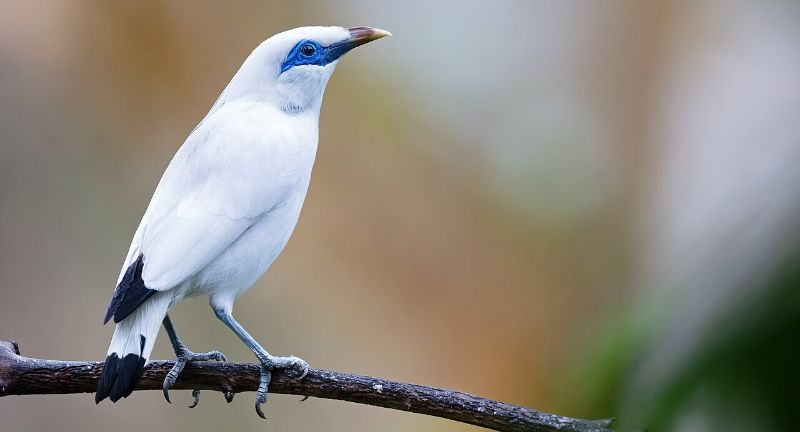
Bali Starling

Wikipedia
The Bali Starling, found exclusively on the island of Bali, Indonesia, is critically endangered, largely because of illegal bird trafficking. Recognized for its stunning white feathers and unique blue skin around the eyes, this species has nearly vanished from its natural habitat. Conservation endeavors involve rigorous crackdowns on the illegal pet trade, initiatives for breeding and reintroduction, and the creation of protected areas. The fight to rescue the Bali Starling from extinction highlights the worldwide battle against illicit wildlife trafficking.
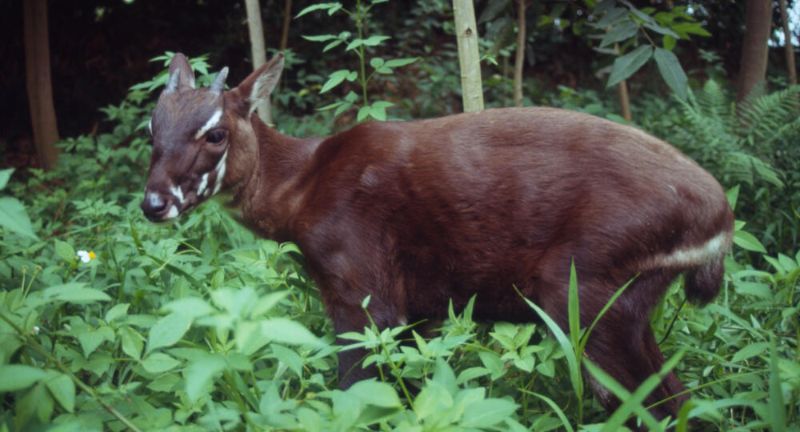
Saola

Wikipedia
The Saola, commonly dubbed the “Asian Unicorn,” is a mysterious and critically endangered species identified in 1992 within the Annamite Range spanning Vietnam and Laos. Recognized for its unique long horns and elusive behavior, encountering the Saola in the wild is exceedingly rare, and its population size remains unknown. Facing perils from habitat destruction and poaching, especially for traditional medicine and trophy hunting, conservation endeavors are complicated by the Saola’s elusive nature. International and local conservation organizations collaborate to preserve habitats and enforce anti-poaching measures, striving to safeguard this extraordinary creature.
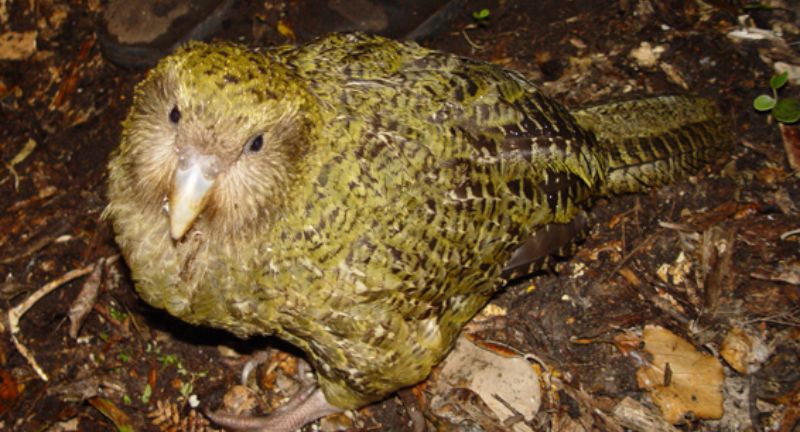
Kakapo

Wikipedia
The Kakapo, a nocturnal, flightless parrot indigenous to New Zealand, is critically endangered, with an estimated population of around 200 individuals. Renowned for its impressive size, distinctive facial disc, and verdant moss-like plumage, the Kakapo faces peril from introduced predators such as cats and rats. Conservation initiatives, including predator-free island refuges and a meticulous breeding regimen, have contributed to stabilizing the population. The ongoing efforts to revive the Kakapo underscore the critical role of human intervention in rescuing species teetering on the brink of extinction.
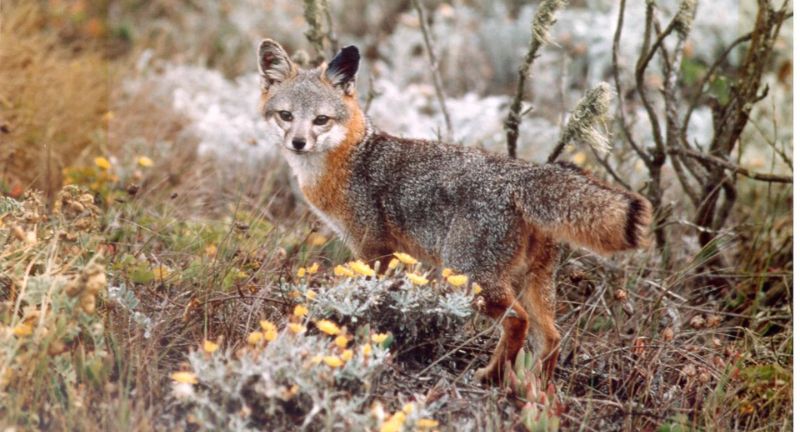
Island Fox

Wikipedia
The Island Fox, indigenous to the Channel Islands off the coast of California, has undergone a remarkable resurgence from the brink of extinction thanks to dedicated conservation endeavors. This diminutive fox species was imperiled by disease and predation from non-native animals, resulting in a steep decline in population numbers. Conservation tactics such as vaccination campaigns, removal of predators, and captive breeding and reintroduction programs have been instrumental in its recovery. The success story of the Island Fox serves as a compelling testament to the effectiveness of focused conservation efforts in reversing the decline of endangered species.
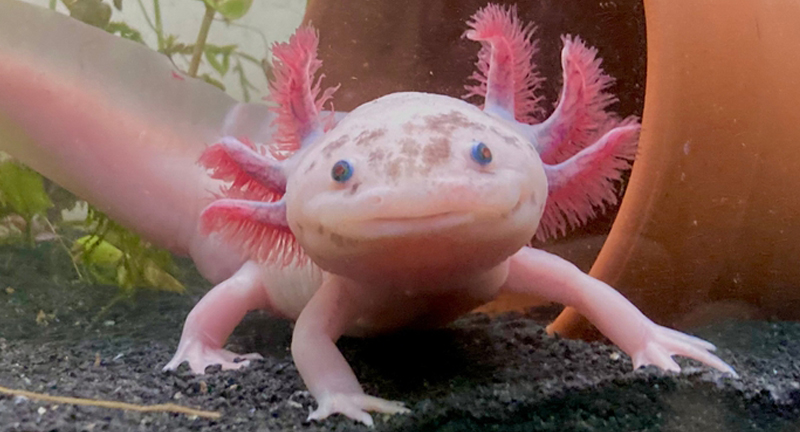
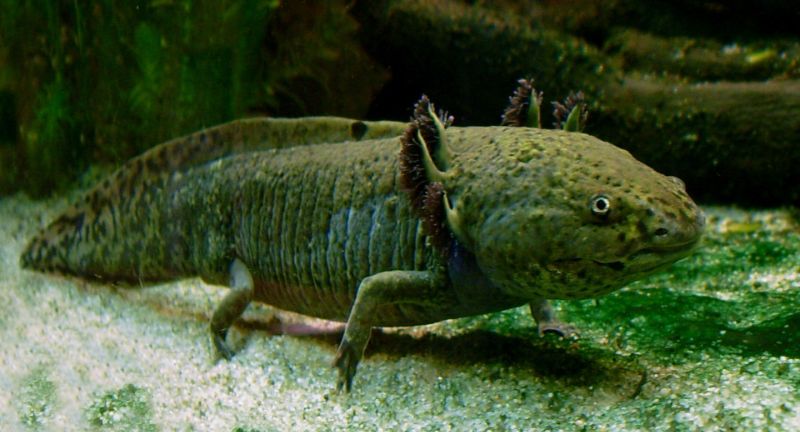
Axolotl

Wikipedia
The Axolotl, known for its extraordinary ability to regenerate and its unique appearance, is native to the Xochimilco lake complex near Mexico City. This species faces threats from urban sprawl, water pollution, and the invasion of non-native species, resulting in a drastic decrease in its natural habitat. Conservation efforts are aimed at rehabilitating their environment and implementing breeding programs to increase their population in the wild. The plight of the Axolotl highlights the impact of environmental degradation on aquatic species and emphasizes the importance of conservation actions.
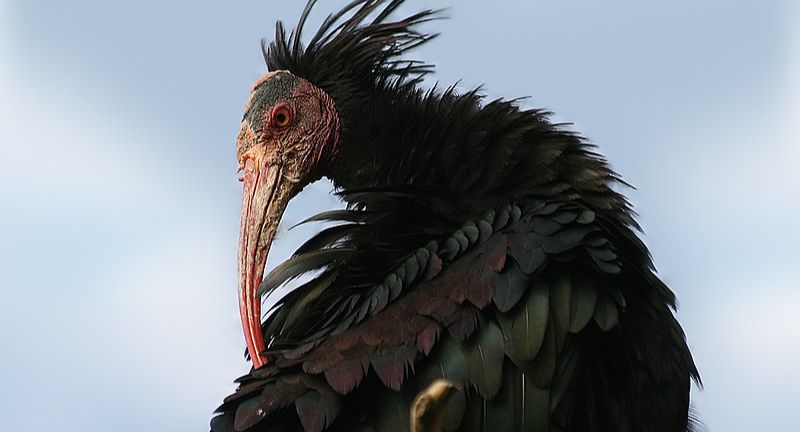
Northern Bald Ibis

Wikipedia
The Northern Bald Ibis, formerly abundant across the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe, is now on the brink of extinction, with a dwindling wild population concentrated mainly in Morocco. Recognized by its unique bald head and elongated, curved beak, this species confronts dangers such as habitat loss, hunting, and contamination from pesticides. Conservation endeavors comprise safeguarding its habitat, implementing breeding initiatives, and reintroducing the ibis to regions it once inhabited. The preservation of the Northern Bald Ibis mirrors the difficulties encountered by migratory birds in today’s era.
Javan Rhino
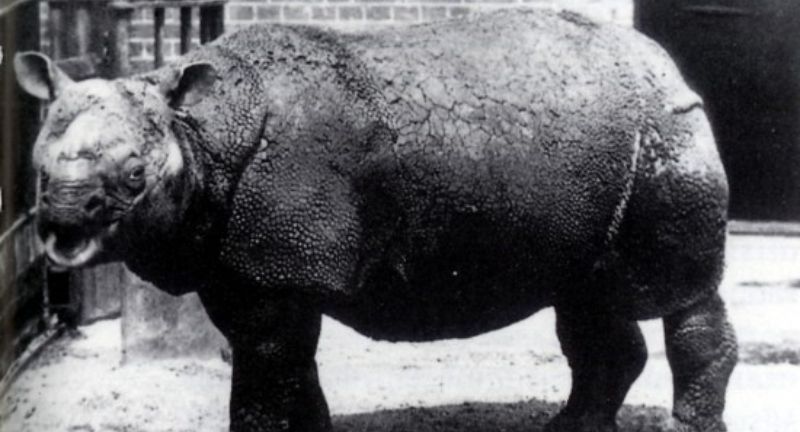
Wikipedia
The Javan Rhino stands as one of the most elusive rhino species globally, with its entire population restricted to Ujung Kulon National Park in Java, Indonesia. This critically endangered species confronts an array of perils, including habitat loss from agricultural expansion and the potential transmission of diseases from domestic animals. With fewer than 100 individuals remaining, it ranks among the most endangered large mammals. Conservation efforts concentrate on habitat preservation, bolstering the rhino population, and mitigating disease transmission risks.
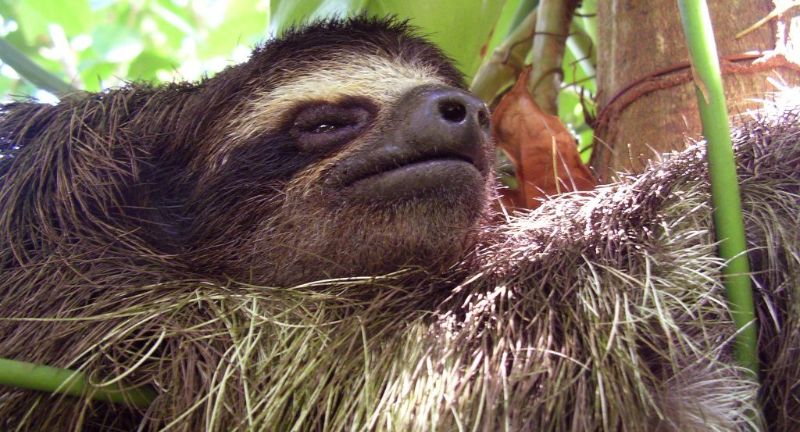
Pygmy Three-toed Sloth

Wikipedia
The Pygmy Three-toed Sloth, unique to Isla Escudo de Veraguas, Panama, faces critical endangerment primarily because of its restricted range and habitat degradation. This sloth species, distinguished by its petite stature and leisurely pace, relies on the island’s mangrove forests for sustenance. Conservation initiatives prioritize safeguarding the sloth’s habitat from encroaching development and raising awareness about its vulnerable status. The Pygmy Three-toed Sloth’s battle for existence underscores the significance of conserving distinct ecosystems and their native species.
Pinta Island Tortoise
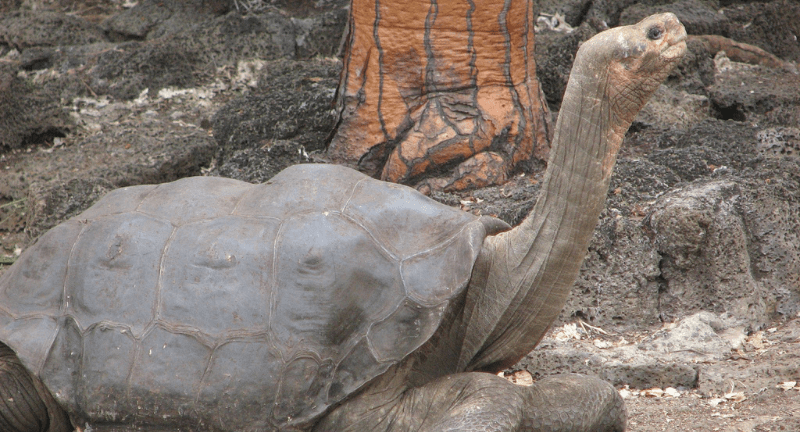

Wikipedia
The Pinta Island Tortoise garnered global interest following the passing of Lonesome George, the sole known member of the species. Conservation endeavors persist for other Galápagos tortoise species, emphasizing habitat rehabilitation and breeding initiatives to stave off further extinctions. Lonesome George’s tale serves as a sobering testament to the repercussions of human intervention on species viability. Conservationists remain steadfast in their commitment to safeguarding the remaining Galápagos tortoises, securing the legacy of these emblematic creatures for generations to come.
Forest Owlet
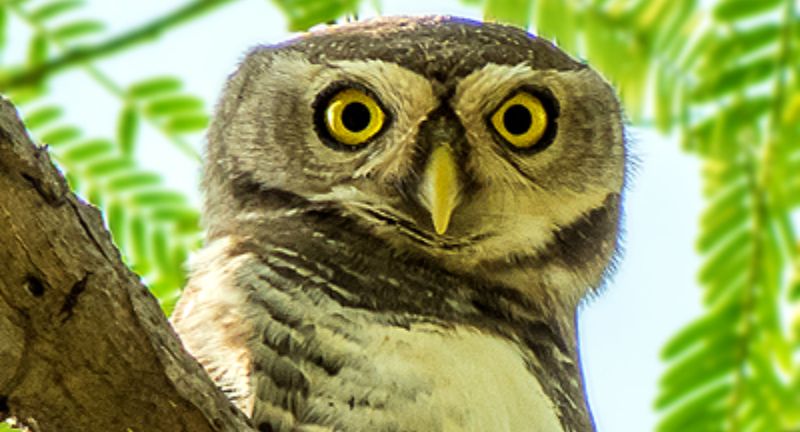

Wikipedia
The Forest Owlet, native to the forests of central India, was believed to be extinct for over a century until its remarkable rediscovery in 1997. This diminutive and critically endangered owl confronts challenges stemming from habitat loss and deforestation. Conservation initiatives prioritize the safeguarding of its remaining habitat and the advancement of research to unravel its ecology and distribution patterns. The resurgence of the Forest Owlet has instilled optimism for the conservation of other “lost” species, underscoring the significance of ongoing exploration and conservation endeavors.
Siberian Crane
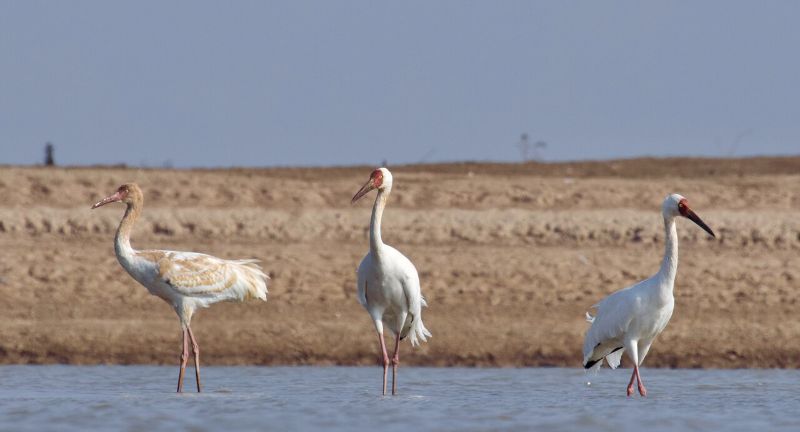

Wikipedia
The Siberian Crane, distinguished by its dazzling white feathers and elongated legs, is critically endangered, largely due to habitat loss along its migratory path from Siberia to China and Iran. Conservation endeavors concentrate on safeguarding crucial stopover and wintering grounds, alongside breeding initiatives aimed at bolstering population numbers. The Siberian Crane’s extensive annual migration represents one of the longest journeys undertaken by any bird species, necessitating a multifaceted, international approach to conservation. The preservation of the Siberian Crane holds paramount importance for the well-being of wetland ecosystems throughout Asia.
Addax
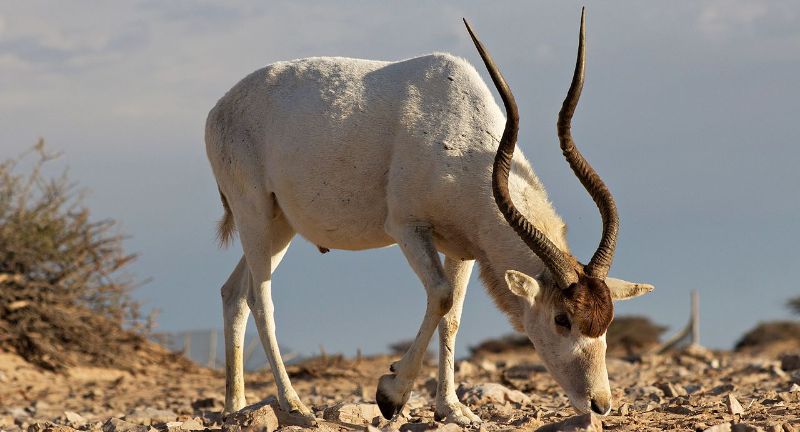

Wikipedia
The Addax, recognized as the white or screwhorn antelope, faces critical endangerment, finding its final sanctuary in the Sahara Desert. Relentless hunting and habitat depletion from industrial and agricultural expansion have precipitated a steep decline in their numbers. Conservation efforts entail establishing protected zones within their habitat and implementing captive breeding programs to facilitate their reintroduction into natural habitats. Renowned for its resilience in harsh desert environments, the Addax symbolizes the importance of conserving desert biodiversity.
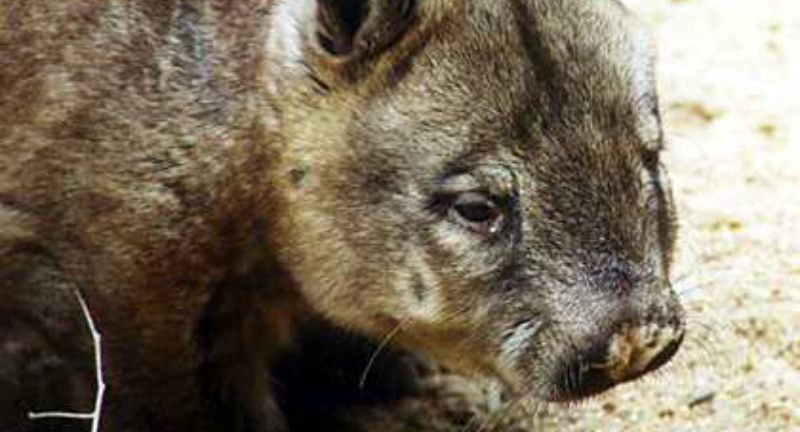
Northern Hairy-Nosed Wombat

Wikipedia
The Northern Hairy-Nosed Wombat, one of the planet’s most uncommon large mammals, exclusively inhabits Epping Forest National Park in Queensland, Australia. This species stands out for its larger stature and plush, silkier fur in contrast to other wombats. Confronted with dangers stemming from habitat deterioration and food source competition, the survival of this species hinges on initiatives centered on habitat preservation and restoration. Conservation initiatives prioritize expanding the wombat’s habitat and shielding the population from predators and diseases.
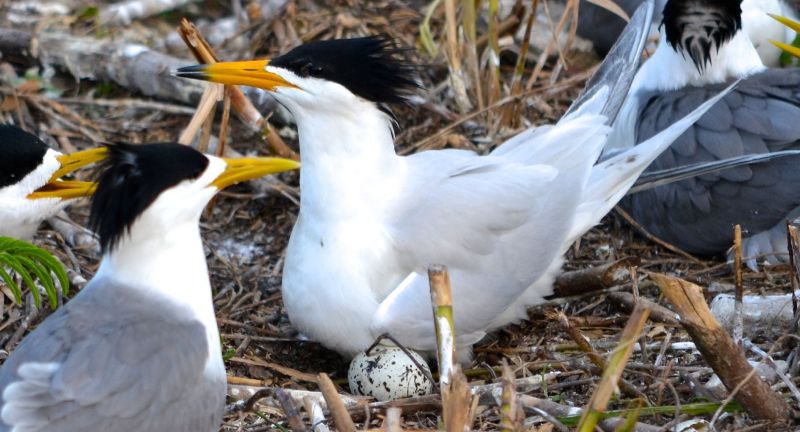
Chinese Crested Tern

Wikipedia
The Chinese Crested Tern, characterized by its dramatic black crest and vibrant orange beak, is a critically endangered seabird with fewer than 100 individuals left. Challenges such as habitat loss, egg collection, and human disturbance jeopardize its existence. Conservation endeavors have focused on habitat rehabilitation and safeguarding nesting areas, resulting in a modest rise in their population. The perilous state of this bird highlights the necessity of global collaboration in avian conservation endeavors.
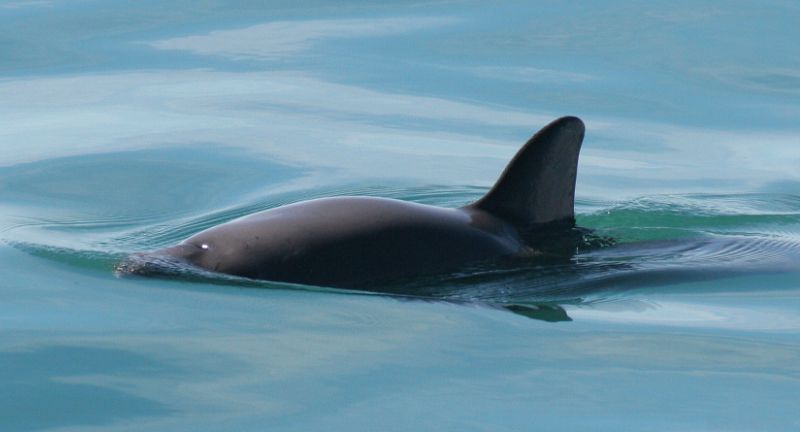
Vaquita

Wikipedia
The Vaquita holds the unfortunate title of being the most endangered marine mammal globally, residing solely in the northern Gulf of California. With their numbers plummeting rapidly, these diminutive porpoises confront extinction primarily due to illicit gillnet fishing targeting the totoaba fish, prized for its swim bladder. Conservationists are in a race against time, employing surveillance and net removal endeavors to safeguard the remaining Vaquita population. The desperate situation of the Vaquita emphasizes the urgent requirement for international collaboration to enforce fishing regulations and implement conservation measures.
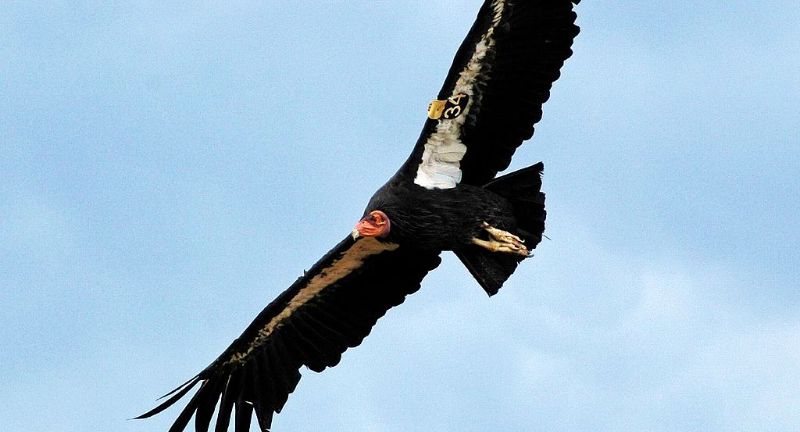
California Condor

Wikipedia
The California Condor stands as a remarkable testament to the triumph of conservation endeavors, having been rescued from the edge of extinction through captive breeding and release initiatives. Once numbering in the thousands, this iconic North American bird faced perilous decline in the 20th century due to poaching, lead poisoning, and habitat degradation. Through dedicated management efforts, including the adoption of lead-free ammunition in condor territories, their population has seen a resurgence. The successful recovery of the California Condor underscores the capacity for human intervention to reverse the plight of endangered species.
Gharial
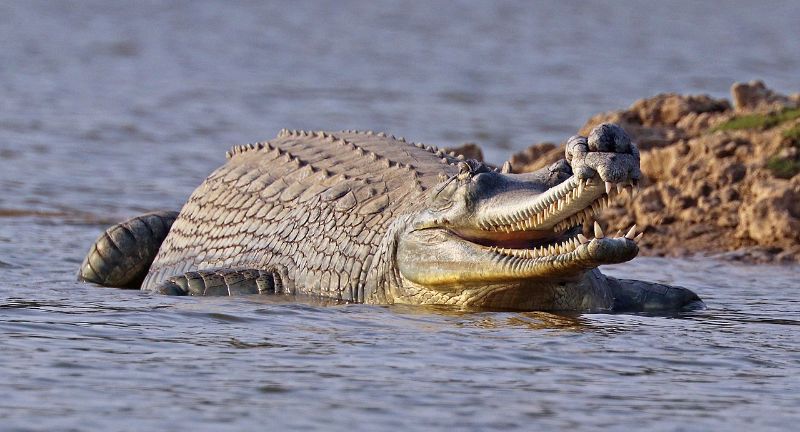

Wikipedia
The Gharial, a critically endangered crocodile species recognized for its elongated, narrow snout, is indigenous to the rivers of the Indian subcontinent. Their population has significantly dwindled due to habitat destruction, pollution, and harmful fishing methods. Conservation initiatives encompass the creation of gharial sanctuaries, captive breeding and release programs, and community education aimed at mitigating human-gharial conflicts. The preservation of the Gharial is essential for upholding the ecological equilibrium of river ecosystems.
Spoon-billed Sandpiper
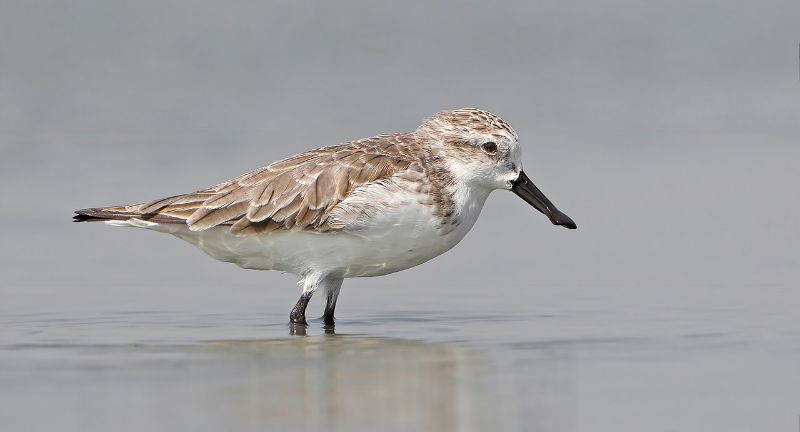

Wikipedia
The Spoon-billed Sandpiper, characterized by its distinctive spoon-shaped bill, is a small bird on the brink of extinction, experiencing a rapid decline in population. Habitat loss in its breeding grounds in northeastern Russia and wintering sites along the coast of Southeast Asia presents significant threats. Conservation measures involve safeguarding habitats, tracking migratory routes, and implementing captive breeding programs to bolster their numbers. The precarious situation of the Spoon-billed Sandpiper underscores the complexities associated with conserving migratory bird species.
Hawaiian Monk Seal
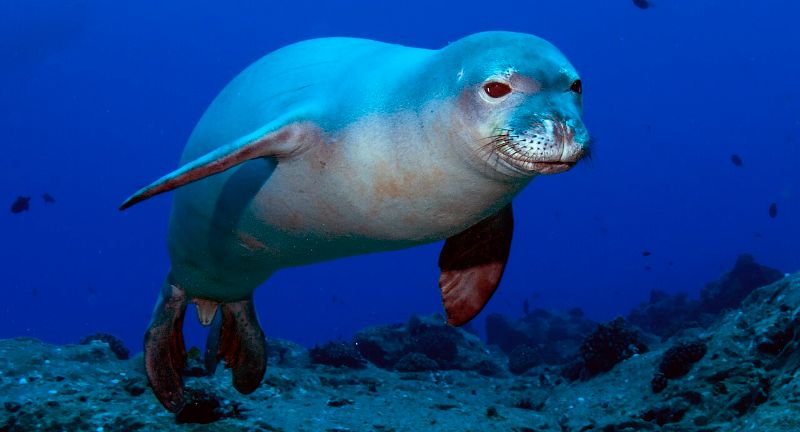

Wikipedia
The Hawaiian Monk Seal is a rare seal species, uniquely adapted to tropical waters and primarily residing in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Despite their population numbering around 1,400 individuals, they face critical endangerment due to human encroachment, entanglement in fishing gear, and the impacts of climate change. Conservation endeavors encompass habitat preservation, rescue and rehabilitation of injured seals, and community education initiatives aimed at mitigating human-induced threats. Protecting the Hawaiian Monk Seal is crucial for sustaining the biodiversity of Hawaii’s marine ecosystems.
Conclusion

Wikipedia
As our journey through the thirty rarest animal breeds draws to a close, it becomes clear that the battle to rescue these extraordinary creatures from the edge of extinction transcends mere conservation; it embodies our stewardship of our planet’s remarkable biodiversity. Each species, with its distinct role in the ecosystem, contributes to the intricate harmony of nature. Their trials and triumphs in the face of adversity serve as a source of inspiration, fostering a deeper reverence for the natural world and a heightened commitment to its protection. Let us carry forth the message of conservation, recognizing that the survival of these rare breeds is intricately intertwined with our own future. This compels us to take action now, safeguarding the diverse tapestry of life on Earth for generations to come.
More Amazing Animals+
-


30 Most Adorable Animals In The World (According To Us)
-


More – Alligator arrest outside of a school in Charleston,…
-


25 Unusual But Undeniably Adorable Baby Animals
-


20 Amazing Facts About Alpacas and Llamas
-


Who Knew? 33 Reasons Rats Are the Perfect Pet
-


25 Reasons Badgers Are Some of the Toughest Animals on…
-


Otterly Adorable: 23 Reasons Why Otters Are More Than Just…
-


Secrets of the Squirrel Kingdom: 25 Amazing Facts
-


We Promise This Animal Is Not As Annoying As You…
-


Baby shark, baby shark, 15 baby sharks: zoo welcomes massive…
-


Goats Ushered Across a Road to Aid in California Fire…
-


Vitakraft’s Squeezable, Hand-Fed Snacks Named Best Cat Treat of 2022
